Overview: What is scabies?
Scabies referrs to a disease that occurs all over the world and can affect people of all ages. It has nothing to do with a lack of personal hygiene, but a lot to do with close physical contact: To get scabies, you have to be close to someone who already suffers from scabies. The infected person may have scabies in the early stages without knowing it – the typical signs of scabies often only appear after some time.
Scabies is triggered by mites that dig small channels in the top layer of the skin. There they lay eggs and leave behind excretions to which the human immune system reacts with very itchy skin changes.
How many people are affected by scabies is unknown, as scabies is not a notifiable disease. In Switzerland and other countries, however, doctors have been observing an increase in cases for several years.
Scabies in children
“Don’t scratch!” That is easier said than done. When children suffer from very itchy skin, they are often warned not to irritate the affected areas further. Parents know that scratching can make the itching worse. And they suspect that the children’s fingernails are by no means sterile. Scratching can cause itch mites to spread on the skin, and scratched wounds become a gateway for bacteria. Rapid medical help for scabies is therefore important in order to stop the disastrous processes.
Doctors have recently observed an increase in scabies in nurseries and schools. Children often have close and prolonged contact with each other – a welcome opportunity for scabies mites to move from one skin surface to another. Where they then begin their work anew. Once a diagnosis of scabies has been made, it is not only the sick child that needs to be treated, but all those who are in close contact with the child. So mostly the family members. This is the only way to prevent the further spread of scabies.
Diagnosis: How can you recognize scabies?
The first step in scabies treatment is to recognize the scabies. However, this is difficult for medical laypersons. At first glance, there often seems to be no difference to other skin diseases, for example eczema in the case of allergies or neurodermatitis.
A magnifying glass with integrated lighting, a so-called dermatoscope, helps the doctor with the diagnosis. When this magnifying device is placed on the skin, itch mites or their burrowed channels can be recognized in many cases. If this is not possible, medical staff can examine a sample of the contents of the ducts under a microscope. Here they often see the mites or their eggs and excretions – visible evidence of scabies.
Scabies rash with bark scabies
A particularly severe form of scabies is the so-called bark scabies (Scabies crustosa or Scabies norvegica). The scabies symptoms appear over a large area and extend beyond the normally affected skin regions. The inner surfaces of the hands and feet are calloused and affected by scales. A consolation for those affected: The itching usually associated with scabies is significantly less severe or even completely absent in bark scabies.
Bark scabies is particularly contagious. It often occurs in nursing home residents whose immune system is weakened. While there are normally around a dozen scabies mites in the skin of people affected by scabies, there can be hundreds or thousands in the case of scabies crustosa. Therefore, even brief skin contact is often enough to become infected.
Cause of scabies: How does scabies develop?
Scabies is caused by direct and close skin contact with a person who is already infested with scabies. Scabies is caused by tiny parasites (scabies mites) that leave eggs and excretions on and in the skin. These foreign bodies cause a reaction of the human immune system, which manifests itself in the form of a skin rash and severe itching.
A quick handshake, a kiss left and right on the cheek is not enough to get infected. Skin contact must last for several minutes because the mites move very slowly and cannot jump from one person to another like a flea.
Scabies mites: tiny but nasty
They are barely visible to the naked eye: Female scabies mites are only 0.3 to 0.5 millimeters in size. After they have been fertilized on the human skin surface by the smaller males and these die, the females begin their work. They dig tunnel-like tunnels in which they can survive for up to two months. This is where they lay their eggs, from which larvae hatch after two to three days. They swarm out and look for skin folds and depressions in which new mites grow after about two to three weeks.
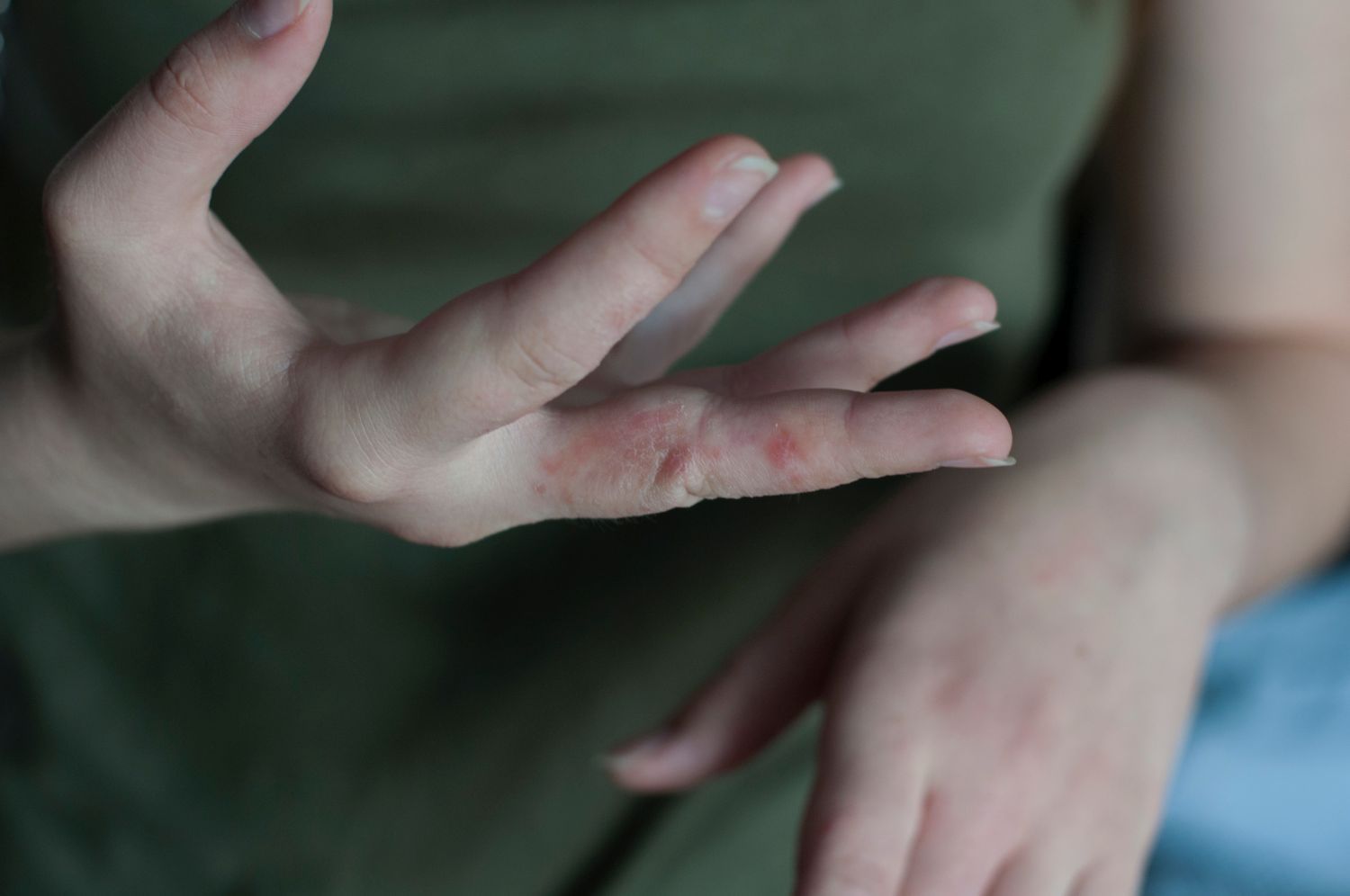
Symptoms of scabies
Severe itching, unpleasant burning, annoying skin rashes – these are the typical signs of scabies. Especially at night in a warm bed and on warm parts of the body, those affected begin to itch even in the early stages of scabies. The need to scratch usually arises in places that the itch mites particularly like to visit:
- Spaces between fingers and toes
- Wrists
- Wrinkles in the armpit
- Elbow bend
- Areola
- Area around the anus
- Genitals, esp. Penis shaft and glans
In infants and small children, the scabies skin picture often also shows that the face, hands and soles of the feet are affected.
Online skin check: Quick and convenient from home
Send a photo of the affected skin area and fill out the short questionnaire. Within 24 hours on weekdays, you will receive a reliable diagnosis from our experts. Your data will be transmitted to us encrypted and treated confidentially.
Treatment of scabies
Since the cause of scabies is clearly established, it can be treated in a targeted manner. Eczema and the annoying itching do not disappear on their own: scabies therapy is only successful once the causative agents of scabies have been destroyed – i.e. the mites, their larvae and eggs.
Scabies is one of the diseases for which people who have no symptoms are also treated. This is because scabies can be contagious before the first symptoms appear. For this reason, not only scabies patients are often treated in shared flats and communities with frequent and prolonged skin contact, but also their flatmates. The same applies to care institutions and the relevant close contacts.
Scabies therapy from the outside
In the external (local) treatment of scabies, the active ingredient permethrin is often applied to the entire body (excluding the face in adults), usually as a cream or solution. The scabies medication kills the parasites and their eggs as a mite poison. It should be washed off thoroughly eight to twelve hours after application. Treatment must be repeated after about 10-14 days.
Any scabies treatment should only be carried out after consultation with a doctor – ideally as soon as the first signs of scabies become noticeable. There are two different ways of treating scabies: external and internal therapy.
Internal treatment of scabies
In the past, creams were mainly used against scabies in Switzerland, but studies have shown that tablets are often more effective. A proven scabies medication is ivermectin; the active ingredient is swallowed in the form of a single tablet. The scabies treatment must be repeated after about 10-14 days.
Scabies is often treated in combination, with creams and tablets.
Are there home remedies for scabies?
I think I have scabies: What should I do? This is usually the first question people ask themselves when they are tormented by itching. The clear answer is: whatever the symptoms of scabies, they should only be treated by a doctor. This is because simple household remedies, such as cooling ointments, cannot eliminate the cause of scabies.
Nevertheless, those affected should ensure that no new outbreaks occur during and after scabies treatment:
- Scabies mites can hide in fabrics that come into intensive contact with the skin. The textiles should therefore be washed at 60 degrees celsius.
- If this is not possible, the parasites can also be killed by placing the laundry in well-sealed plastic bags at room temperature for at least 48 hours.
- Upholstered furniture should be thoroughly vacuumed and, if possible, not used for four days.
Prognosis: How does scabies progress?
When mites cause scabies, it takes a while for those affected to notice: Two to five weeks can pass before the skin reacts and itches after the parasite infestation. This is how long it takes the body’s own defense cells to respond to the intruders with an immune reaction the first time. The second time and with further mite attacks, the immune system already knows the parasites and reacts more quickly – the signs of scabies can be felt after just a few days.
The itchy skin is reddened, with pinhead-sized blisters and raised pustules. The type of skin lesions that cause scabies is not always the same. In some cases, the curved ducts of the scabies mites or even the animals themselves may become visible.
Even though scabies is not a dangerous disease, complications can occur during the course of scabies. If the skin is severely inflamed and open, bacteria can penetrate and cause infections.
Even after successful scabies treatment, the itching usually persists for several weeks. The same applies to the skin rash, medically known as post-scabies eczema. Ointments and creams prescribed by a doctor can provide relief for those affected – until the issue of scabies is finally resolved.
Details of the treatments