When does the prostate need to be operated on?
Prostate surgery can be considered as a treatment option if benign enlargements block the flow of urine and medication does not bring any improvement, or in the case of prostate cancer if it is confined to the prostate.
What prostate problems are there?
Prostate problems can include various conditions, including benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH, benign enlargement of the prostate), prostatitis and prostate cancer. These conditions can lead to symptoms such as an increased urge to urinate, pain in the pelvic area and problems urinating. It is important to consult a doctor if symptoms occur in order to obtain an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Problems with the prostate can be treated. Do not accept this as part of the ageing process. Get active!
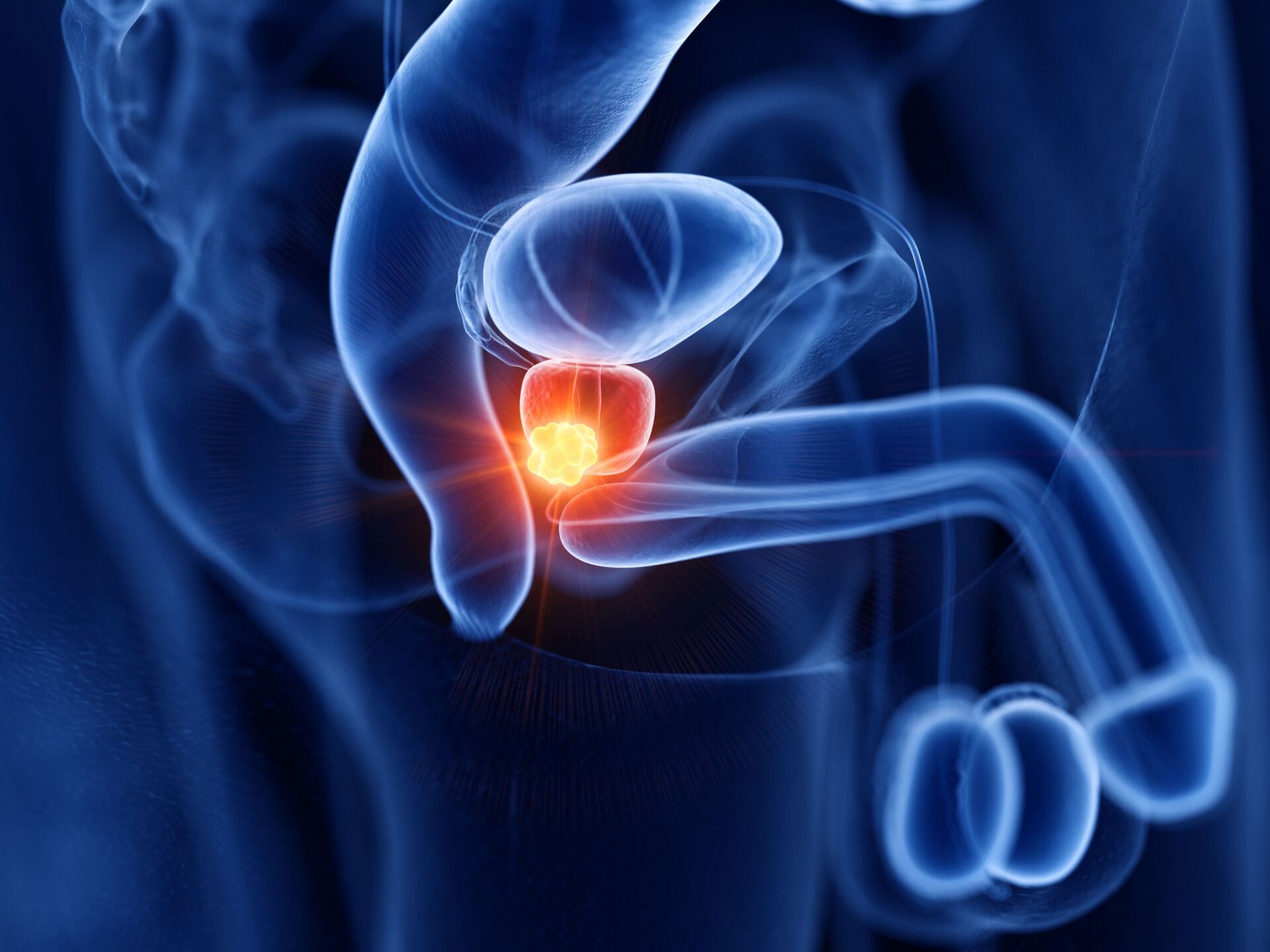
What is a prostate and where is it located?
The prostate is a sex gland in the male reproductive system that lies directly under the bladder and surrounds the initial part of the urethra. It is roughly the size and shape of a chestnut. The prostate produces a secretion that forms an essential component of semen.
What does the prostate do?
The prostate produces a secretion that helps to nourish and protect the sperm in the ejaculate. This fluid makes up a significant part of the ejaculate and helps to make it thin and protect the sperm in the acidic environment of the vagina. In addition, the position of the prostate and the muscle-controlled internal changes in shape ensure that either only sperm or only urine comes out of the penis.
How do you recognize prostate cancer?
Prostate cancer is detected at an early stage using blood tests such as the PSA test (prostate-specific antigen) or the Stockholm3 test. Symptoms usually only appear at a later stage and can include difficulty urinating, frequent urination, pain when ejaculating or blood in the urine or semen. If you have these symptoms, please see your doctor immediately. We recommend that men should have regular prostate checks from the age of 50, and from the age of 45 if they have a family history of prostate cancer (father, brother with prostate cancer).
What to do with prostate cancer?
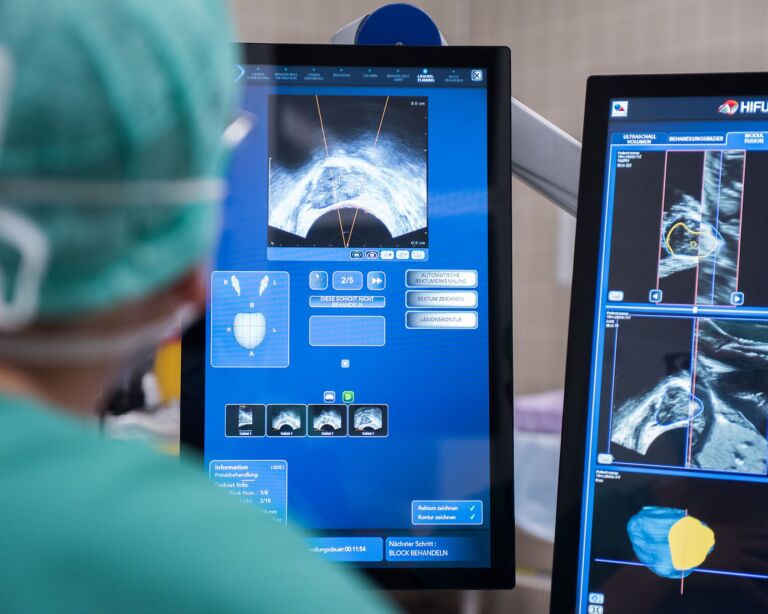
The treatment of prostate cancer depends on the stage of the cancer, the histological classification, the patient’s state of health, age and personal preferences and life situation. Prostate cancer treatment can include radical removal of the prostate, focal therapy such as HIFU (High Intensity Focal Ultrasound), radiotherapy, hormone therapy, chemotherapy or a combination of these treatments. Active surveillance may be an option if the disease progresses slowly at an early stage.
What helps against prostate cancer?
Prostate cancer is primarily treated with medical treatments such as surgical removal of the prostate, focal therapy such as HIFU (High Intensity Focal Ultrasound), radiotherapy, hormone therapy and, if necessary, chemotherapy. If the disease is not very aggressive and at an early stage, it can be monitored closely (active surveillance) rather than actively treated. Accompanying measures such as a healthy diet, sufficient exercise and psychological support can support the success of treatment.
Can the prostate be removed?
Yes, the prostate can be surgically removed. This surgical procedure is known as a radical prostatectomy. A prostatectomy is a treatment option for cancer that is confined to the prostate (localized) and has not metastasized. The entire prostate is removed. We do this using robotic surgery with the DaVinci surgical robot.
You can live well without a prostate. Side effects such as incontinence and erectile dysfunction may occur for some time after the procedure. Continuous pelvic floor training, which begins before the operation, can provide very good support.