Swiss HPB Center
Liver cancer and liver metastases are treated at the University Hospital Zurich (USZ) by highly qualified specialists in collaboration with all medical departments. These include liver surgery, hepatology and gastroenterology, oncology, radiotherapy and radiology. The USZ offers the latest and most effective treatment options for liver tumors and is also a certified liver cancer center. The treatment of all patients is embedded in the structures of the Liver Tumor Center at the Comprehensive Cancer Center Zurich (CCCZ) and the Swiss Center for Liver, Pancreatic and Biliary Tract Diseases (Swiss HPB Center). Patients with liver tumors are discussed with all medical disciplines at a tumor board specially designed for liver tumors. The optimal and individual treatment is determined for each patient.
Liver resection and portal vein embolization
The treatment of liver metastases has benefited from a large number of innovations. However, liver surgery (liver resection) is still the best option for the long-term survival and cure of secondary liver tumors by removing the liver metastases. Extensive tumor burdens and metastases, traditionally considered inoperable, are now amenable to curative treatment by systemic conversion chemotherapy, followed by a variety of interventions such as enlargement of the healthy liver by portal vein occlusion, staged surgery or ablation modalities.
In contrast to all other solid organs, the liver can rebuild a new, fully functional tissue mass (liver regeneration) within a short time after a major tissue loss, such as during an operation. This ability is the basis for the feasibility of large hepatectomies (liver resections), in which up to 80 % of the liver tissue is removed from patients with healthy livers. The main obstacles to early liver surgery were uncontrolled bleeding during resection and insufficient liver volume or insufficient liver function. The use of anesthesia with low central venous pressure, occlusion of the inflow (e.g. with the Pringle maneuver), improvements in transection techniques and a precise knowledge of the segmental liver anatomy were central to the progress of modern liver surgery.
Portal vein embolization (PVE) to enlarge the residual liver
In critical cases, preoperative preparation (about 3 weeks before the operation) is sometimes necessary. If the residual volume after resection is too small, the remaining part of the liver is stimulated before the operation by interventional radiologists closing the portal vein on the other side of the part of the liver to be removed (preoperative embolization).
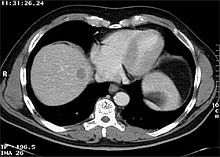
Local removal of a central liver tumor
This leads to a redistribution of blood flow in favor of the remaining portion and thus enables compensatory growth (hypertrophy) before the operation.
Less invasive, laparoscopic procedures are used for diagnostic purposes, to obtain biopsies or in some cases even for partial liver resections.
Local systemic chemotherapy
Local or systemic chemotherapy can be used before surgery in order to make curative resection possible by shrinking the tumor. Postoperative chemotherapy is used for incomplete resection or to prevent recurrence and new metastases.

Pump
In general, chemotherapy can be administered intravenously or locally. Local therapy allows the slow and continuous administration of high doses and is mainly used for advanced liver metastases. For this purpose, a special pump is placed in the body and connected to a blood vessel. The medication is delivered by the pump via this blood vessel.
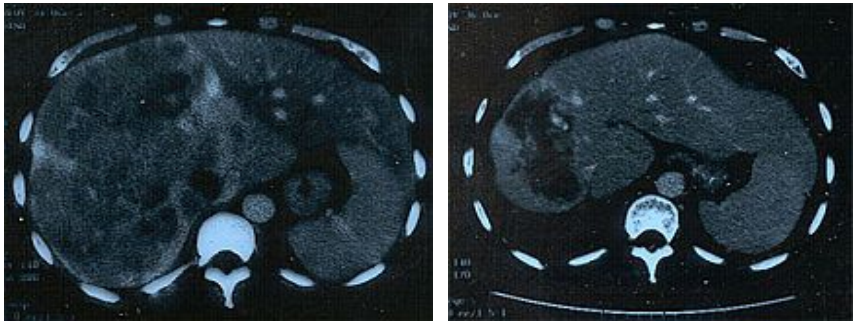
Downstaging of unresectable liver tumors with intra-arterial chemotherapy (CT before and after treatment)
Two-stage liver resections for multiple metastases
However, some patients, particularly those with multiple colorectal liver metastases (CRLM) in which both sides of the liver are affected, require a two-stage surgical procedure. Portal vein ligation (PVL) is a standard procedure to achieve resectability in patients with an inadequate future residual liver (FRL) before planning a subsequent major hepatectomy (liver resection). PVL is actually the first step of a two-stage surgical procedure (liver resection) for the treatment of initially inoperable liver metastases (Reference: Modern therapeutic approaches for the treatment of malignant liver tumors. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020; 17: 755-772):
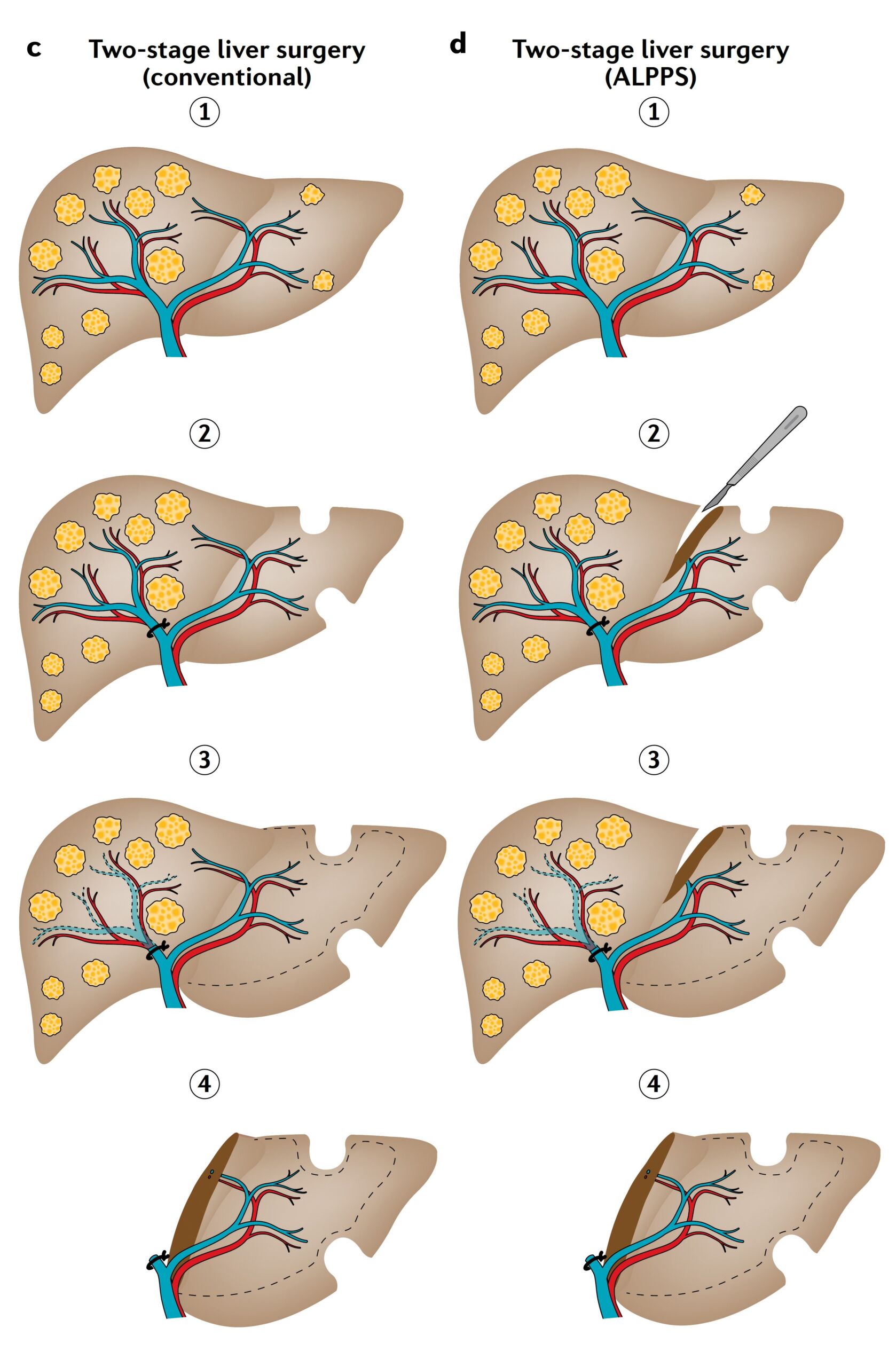
Figure C and D:
Extensive tumor burden, where both sides of the liver are affected (step 1), is often treated with two-stage hepatectomy (liver surgery) either by conventional hepatectomy (partial c) or by combining liver partition and portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy (ALPPS) (part d). In both types of hepatectomy, tumor removal of the liver remnant (FLR) is combined with portal vein ligation in the first stage of the operation (part 2). In ALPPS, the operation is supplemented in the first stage by a liver transsection (part d, step 2). Once sufficient volume hypertrophy has been achieved (step 3) the complete hepatectomy is performed in the second phase (step 4) carried out. While the inter-stage interval for conventional hepatectomy is typically 4-8 weeks (part c, steps 2-4), ALPPS triggers rapid growth so that complete hepatectomy can be performed 7-14 days after the initial surgery (part d, steps 2-4). The size of the initial FLR (dashed line) is projected onto the enlarged FLR to illustrate the effect of volume hypertrophy (parts c-d, steps 3,4).
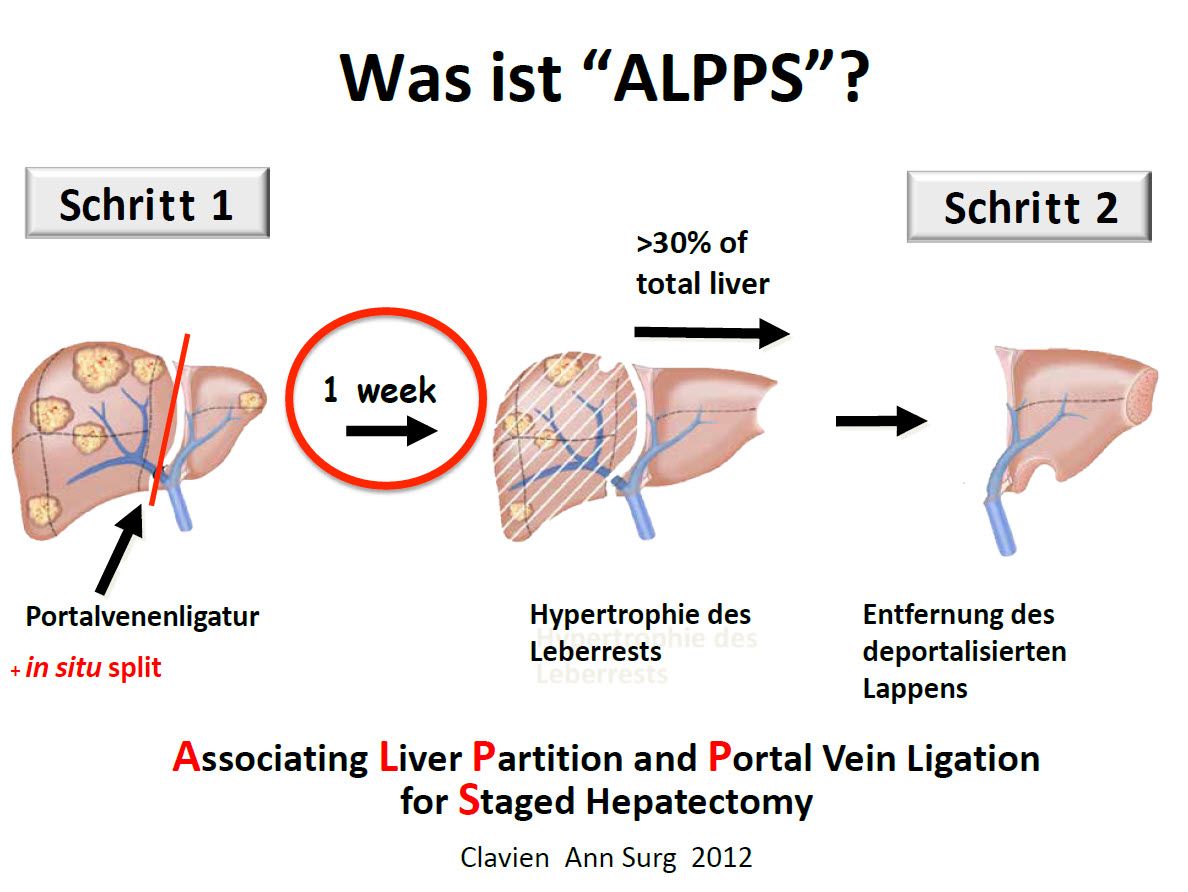
Associating Liver Partition and Portal Vein Ligation for Staged Hepatectomy (ALPPS) to enlarge the residual liver
The new ALPPS liver resection method is also used for liver metastases, which allows up to 80-90% of the total liver to be removed in two operations with a short time interval of 1-2 weeks between the operations in the case of very small residual liver volumes. The growth of the liver is stimulated by dividing the liver without resection in a way that can normally only be achieved after a complete liver resection, without the liver being completely resected. Only in the second step is the affected liver completely resected.
Detailed explanation of the ALPPS operation
NanoKnife
The NanoKnife system uses irreversible electroporation (IRE). This is a new type of technology that involves a series of rapid electrical impulses.
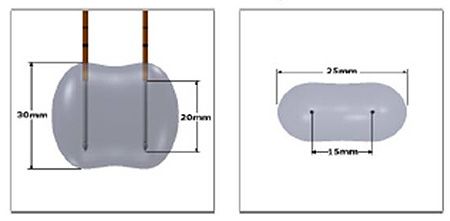
Application of NanoKnife technology: The electricity flows between the electrodes in a dumbbell-shaped field.
These impulses trigger the opening of the cell membranes in the cancer. These pores are permanently disrupted by the high voltage and contribute to the cell death of the cancer cells. The great advantage of the NanoKnife system is the greatly improved protection of tissue, especially nerves, blood vessels and bile ducts, which was not possible with all previous ablation systems such as radiofrequency ablation (RFA) or microwave ablation. Ablation therapies are also used in the treatment of secondary, metastatic liver tumors.
Detailed explanation of the NanoKnife
Aftercare
After treatment has been completed, regular follow-up examinations are important for liver metastases. The follow-up appointments depend, among other things, on the original tumors. They include, for example, a thorough physical examination, an ultrasound scan of the abdomen, a chest X-ray or a CT scan and, if necessary, various blood tests.








