Diagnosis
The serological detection of parasite-specific antibodies is indicative of the diagnosis. In conventional X-ray images, calcifications within a cyst may be visible, but non-calcified cysts are not visualized.
The diagnosis is best made by CT, MRI or ultrasound examinations in conjunction with the serological examination.
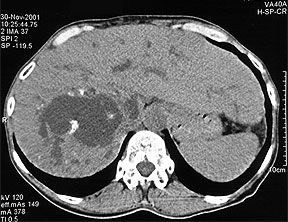
Computer tomogram of Echinococcus cysts in the liver
Treatment
The treatment of choice is complete surgical resection of the lesion, followed by adjuvant therapy with the drug albendazole.
Resectability depends on the following factors, among others:
- Location of the lesion and metastasis formation
- General condition of the patient
- Surgical experience of the medical team
- Long-term treatment with albendazole is indicated for inoperable patients or incomplete resection.
In young patients in particular, we strive for a surgical solution even in the case of extensive findings that are difficult to treat surgically: In Zurich, we recently treated a young woman with Echinococcus multilocularis in whom the fox tapeworm had grown from the liver into the right atrium of the heart. She received a living liver transplant from a relative and, in collaboration with our heart surgeons, a reconstruction of her right heart.

Certificate Publications



