Depending on its form and severity, cataracts can cause various symptoms, mainly reduced visual acuity, fog-like blurred vision, increasing short-sightedness with age, increased glare and shadowy double vision.
Cataract surgery
A cataract is a clouding of the lens. Such opacities can be congenital or develop at any age as a result of accidents, side effects of medication or in the context of general illnesses. Cataracts are by far the most common manifestation of the natural ageing process.
Treatment
Cataract surgery is the most common treatment for cataracts. The cloudy lens is surgically removed and replaced with a completely clear, artificial lens.
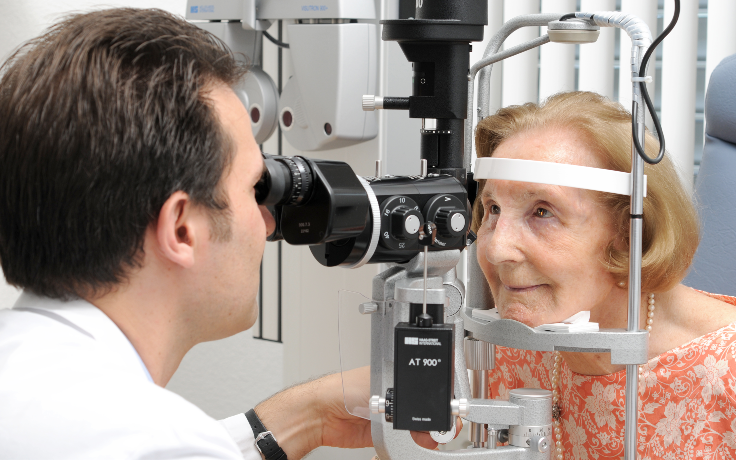
A preliminary cataract examination is carried out before cataract surgery. The eye is measured and examined. The options and chances of an operation are then discussed individually. Even though cataract surgery is a routine procedure today, complications can occur – albeit very rarely – which prolong the recovery time or even impair vision in the long term. For this reason, cataract surgery should only be performed when the patient is clearly impaired by the lens opacity. It is particularly important that the opportunities and risks are discussed in detail with the surgeon.
For patients
As a patient, you cannot register directly for a consultation. Please get a referral from your primary care physician, specialist.