Various treatment options
There are various treatment options for AVM of the brain, which can be used alone or in combination:
- Endovascular embolization: In this procedure, the vascular malformation is reached and treated via the arteries and veins after a groin puncture. During the procedure, we insert plastic tubes (catheters) through the femoral artery into the vessels of the AVM and inject an agent that closes the vessels of the malformation. Endovascular embolization is less invasive than traditional surgery. It can either be used alone or as a preparation before other surgical procedures to reduce the size of the AVM or the likelihood of bleeding and make the procedure safer.
- Surgical removal (resection): The AVM can be surgically removed by a neurosurgical procedure, with or without preoperative embolization.
- Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS): In this treatment, radiation is directed precisely at the AVM. The radiation damages the blood vessels of the AVM and leads to scarring and thus to the destruction of the AVM.
- Conservative treatment: Conservative treatment (without surgery) is also considered as an alternative to invasive methods. This is chosen in certain cases after thorough consideration of the natural risks of the disease compared to the risks/successes of invasive treatment.
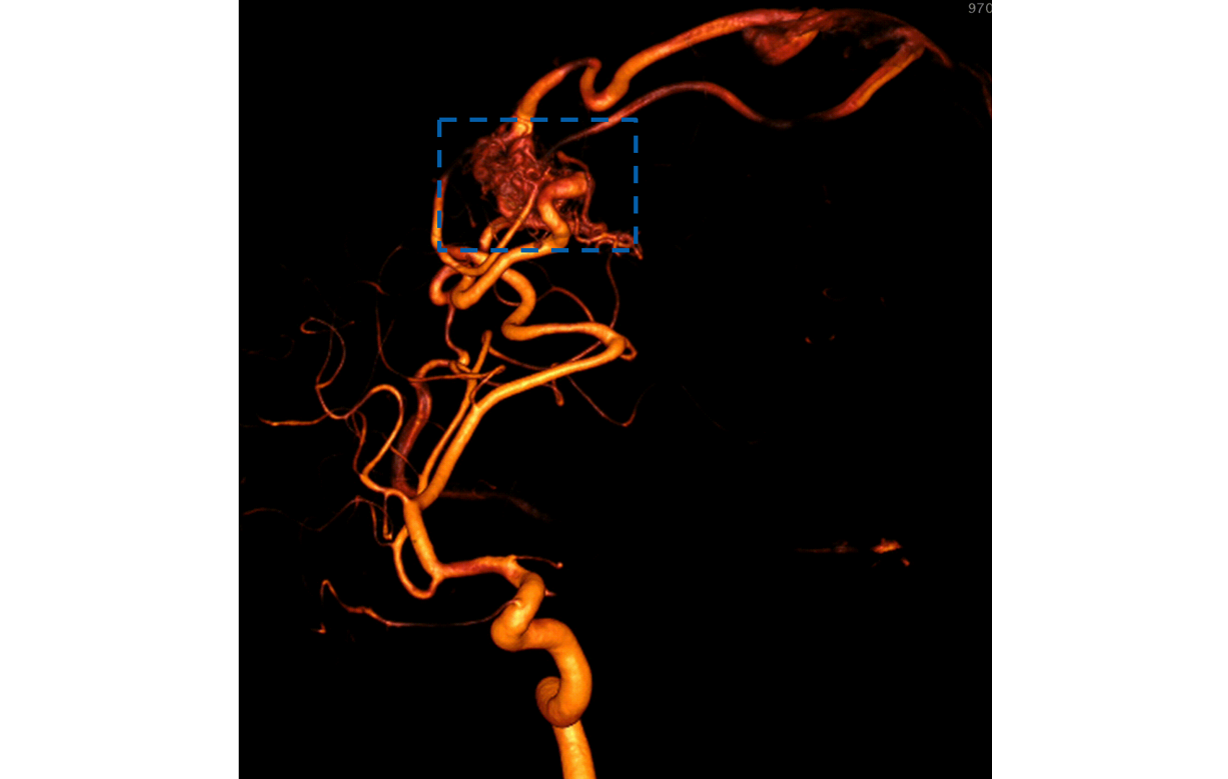
Vascular malformation (arteriovenous malformation) in the blood vessels of the head. The AVM is visible as a vascular tangle.



