Best urology clinic
The Clinic for Urology has been ranked as the best urology specialist clinic in Switzerland in the current ranking of the international news magazine Newsweek “The World’s Best Specialized Hospitals 2025”.
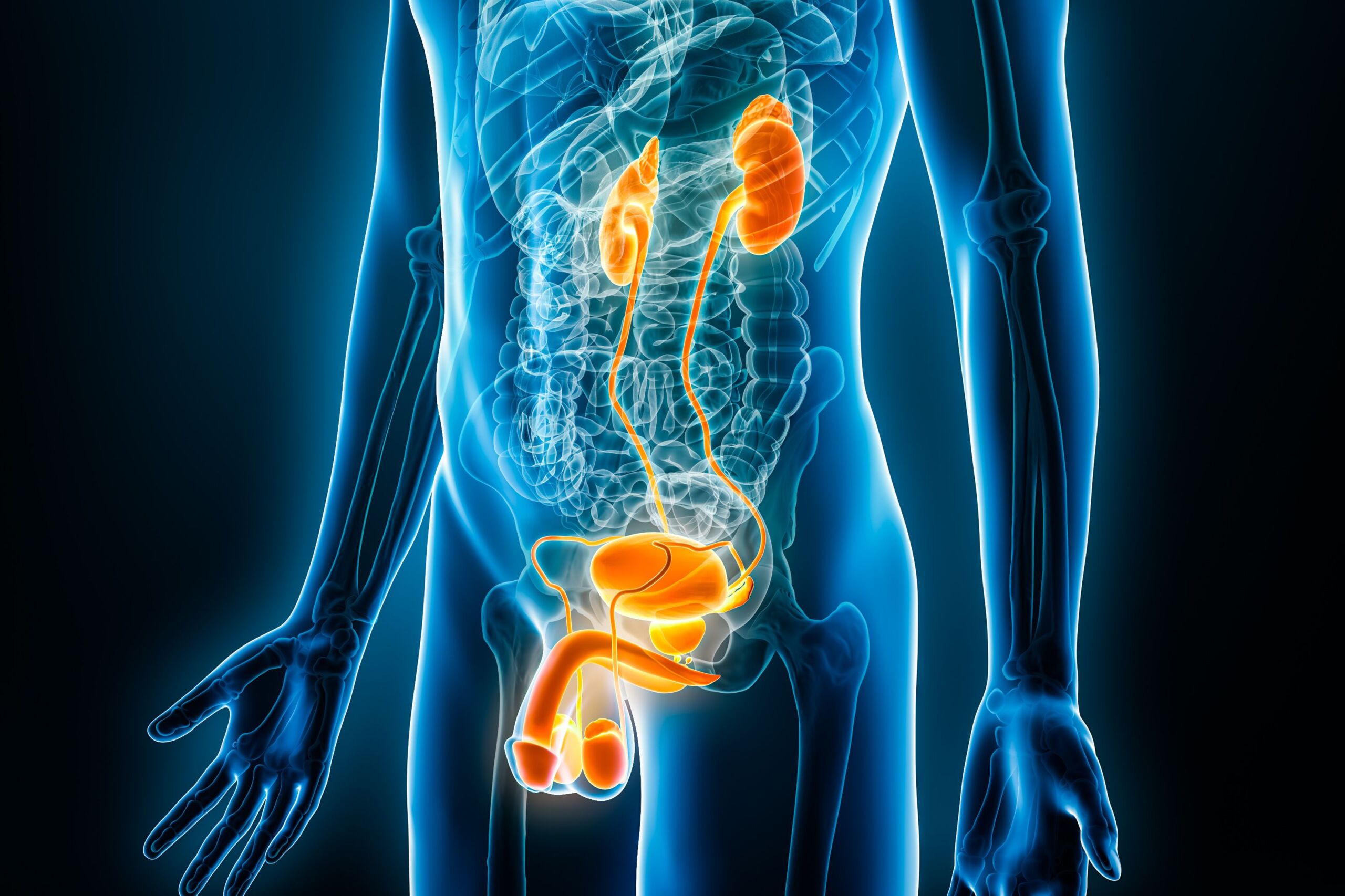
The Department of Urology includes the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of diseases of the urinary tract in men and women, as well as the male reproductive organs.
The Clinic for Urology has been ranked as the best urology specialist clinic in Switzerland in the current ranking of the international news magazine Newsweek “The World’s Best Specialized Hospitals 2025”.
Our urology-specialized physicians address a variety of diseases and conditions, including urinary tract infections, kidney stones, bladder problems, sexual dysfunction and impotence, prostate disease, male infertility and cancers of the genitourinary system. We use a variety of diagnostic procedures, such as ultrasound, cystoscopy, and X-rays, to identify disease and offer a wide range of treatment options, including drug therapies, surgical procedures, and minimally invasive procedures. Two special areas of focus are our certified Prostate Cancer Center and the Continence and Pelvic Floor Center, in which we offer holistic and interdisciplinary diagnostics, therapy and care through a network of specialists.
The Department of Urology treats the entire spectrum of urological conditions with the most modern and innovative diagnostic methods and treatments:
For minimally invasive, precise procedures with very little blood loss and shorter hospital stays, we rely on surgical techniques such as:
We are also certified by the European Board of Urology (EBU) as a training center, as well as by the Swiss Medical Association (FMH) as an A1 clinic for the full FMH further training to become a specialist in urology.
Our highly qualified team of urologists will be happy to advise you on your concerns.
There are several signs and symptoms for which it is advisable to consult a urologist. These include:
Urology deals with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the urinary tract, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. These include, for example, urinary tract infections, kidney or urinary stones, bladder infections and urinary incontinence. Urology also specializes in diagnostic and therapeutic measures of diseases of the male reproductive organs such as prostate diseases, erectile dysfunction, testicular tumors and infertility. Urologists also perform surgical procedures such as removal of kidney stones, treatment of prostate cancer, and correction of congenital deformities.
To the treatmentThe urologist is responsible for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra, and male reproductive organs such as the prostate, testicles, and penis.
No, urology affects both men and women. Urologists specialize in diseases of the urinary tract in both sexes. While certain conditions such as prostate disease exclusively affect men, urologists also treat urinary tract infections, bladder infections, urinary incontinence, kidney stones, tumors of the urinary tract, and other problems that can occur in both men and women.
A urologist may perform examinations in women such as a physical examination of the abdomen, urinalysis, cystoscopy, urodynamics, or ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder. These examinations help in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the urinary tract in women.
During the preventive examination for men at the urologist’s office, also known as urological prevention or urological screening, various examinations are performed. This usually includes a detailed medical interview, a physical examination including the external genitalia, a urine examination, a blood test if necessary, and counseling on individual risk factors. In addition, depending on age and individual risks, further examinations such as a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test or an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder may be carried out. At the USZ, we also offer the new genetic blood test, Stockholm3, for improved early prostate cancer detection.
No, palpation, also called digital rectal examination (DRU) or finger examination, is now performed at the USZ only in cases of increased risk. Here, the urologist palpates changes in the prostate and rectum with a finger through the rectum. Meanwhile, other diagnostic methods are available in urology that are more accurate than palpation. In addition to blood and urine tests, ultrasound and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) are used to identify changes in the prostate.
Urology is a medical specialty that deals with diseases of the urinary tract in men and women, as well as diseases of the male reproductive organs. Urology thus encompasses both urological and andrological aspects.
Andrology, on the other hand, is a branch of urology that deals specifically with the male reproductive organs and their associated diseases and dysfunctions. Andrology focuses on the investigation, diagnosis and treatment of male factors of infertility, erectile dysfunction, hormonal disorders and other specific diseases of the male reproductive system.
A urology consultation usually begins with a medical discussion in which the patient tells the urologist his/her symptoms, complaints and medical history. This is followed by a physical examination in which the urologist palpates specific areas such as the genitals, lower abdomen or kidneys. Depending on requirements, further examinations such as urine and blood tests, imaging procedures such as ultrasound or X-rays or specific tests such as a PSA test or Stockholm3 test for the early detection of prostate cancer can be carried out. Based on the results, the urologist/urologist will make a diagnosis and recommend appropriate medical care or further testing. In many areas, urology works in an interdisciplinary manner with other specialties; therefore, other specialties may also be consulted for further clarification and treatment options.


