Research Group: Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy (ACM) Research (Group leader: Prof. Dr. med. Firat Duru)
The research focus of the Duru Lab at CTEC is to identify circulating and tissue biomarkers for the diagnosis and risk stratification of patients with arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy (ACM).
In addition, the researchers explore and study possible therapeutic strategies in order to halt the active phase and the progression of disease, and hence to prevent potentially life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias and advanced heart failure in these patients. Ongoing research is translational and encompasses experimental and basic science aspects with the ultimate goal for harnessing knowledge from basic science to establish novel strategies for the diagnosis, risk stratification and clinical management of patients with ACM. Moreover, the researchers aim to understand the true impact of the underlying genotype as well as environmental factors, such as exercise, on the clinical phenotype of these patients.
The research group represents a translational extension of the Zurich Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy (ARVC) Program, which was initiated by Prof. Firat Duru and Prof. Corinna Brunckhorst (Director and Co-Director of the Cardiac Arrhythmia Service at the University Heart Center Zurich) in 2011 in an attempt to increase overall understanding of this challenging and life-threatening disease. In early years, the research was solely clinical and single centric, but over the years, there has been increasing focus on understanding its underlying pathophysiology at a translational level. Moreover, the research group has established extensive collaboration with basic and clinical research science partners and institutions within Switzerland and from around the globe. The spectrum of research has also extended from ARVC-only to the broader group of patients with various forms of ACM and its overlapping syndromes.
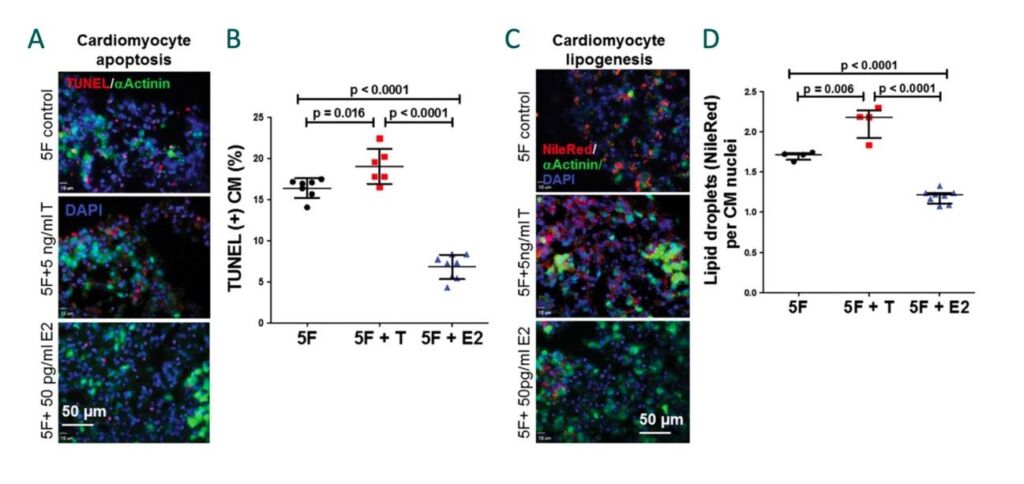
Figure 1. Cardiomyocyte apoptosis is increased by testosterone and decreased by estradiol in ARVC/D iPSC-CMs. (A) Representative images showing that testosterone (T) increased and estradiol (E2) decreased cardiomyocyte (CM) apoptosis (apoptosis shown by TUNEL+ staining in red). (B) Cumulative quantitative data of CM apoptosis. Cardiomyocyte lipid accumulation is increased by testosterone and decreased by estradiol in. (C) Representative images showing that testosterone (T) increased and estradiol (E2) decreased lipid accumulation (Nile Red-positive lipid droplets). (D) Cumulative quantitative data of CM lipogenesis.
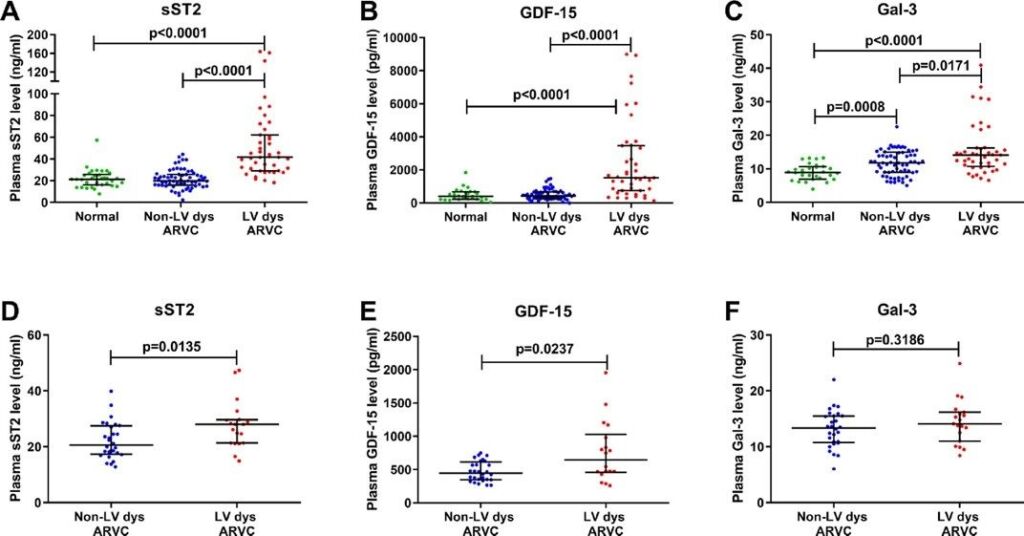
Figure 2. Novel plasma biomarkers predicting biventricular (BiV) involvement in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC): Plasma levels of sST2, GDF-15 and Gal-3 in ARVC patients with BiV involvement versus RV involvement Plasma sST2, GDF-15 and Gal-3 levels of ARVC patients with RV and BiV involvement in the discovery cohort (n =108) A-C and the validation cohort (n = 47) D and F. Individual data plotted with mean ± SEM. P- values calculated using Mann-Whitney-U-Test
Ongoing research lines
- Identification of circulating and tissue biomarkers for diagnosis and risk stratification of ACM and overlapping diseases.
- Studying the impact of gender and sex hormones on arrhythmic and heart failure outcomes on ACM and the role of physical exercise on hormone levels.
- Investigation of the impact of various desmosomal and non-desmosomal mutations on disease phenotypes.
- Determining the level of myocardial injury during physical exercise in ACM patients
- A comprehensive multiomics approach to find an integrated perspective on genotype-phenotype relationship in ACM and to improve diagnosis and risk stratification.
- Studying the determinants of ACM during hot phases of disease
- Investigating the role of autoimmunity in ACM.
Collaborations
National
- Department of Biosystems Science and Engineering, ETH, Basel (Andreas Hierlemann, Jihyun Lee)
- Swiss Institute of Allergy Research / SIAF, UZH, Davos (Cezmi Akdis, Willem van de Veen)
- Swiss DNAlysis, Zurich (Argelia Medeiros)
- Department of Molecular Sciences, UZH (David Penton Ribas)
International
- Johns Hopkins / US ARVC Program (Hugh Calkins, Cynthia James)
- Fuwai / Chinese ARVC Program (Jiangping Song, Liang Chen)
- Dutch ARVC Program (Richard Hauer, Peter van Tintelen)
- Canadian ARVC Program (Julia Cadrin-Tourigny)
- Italian ARVC Program (Domenico Corrado, Claudio Tondo)
- UK ARVC Program (Alexandros Protonotarios)
- French ARVC Program (Philippe Chevalier)
- Scandinavian ARVC Program (Pyotr Platonov)
- Australian ARVC Program (Christopher Semsarian)
Research Team
- Corinna Brunckhorst, MD
- Deniz Akdis, MD
- Sarah Costa, MD
- Gonca Suna, MD, PhD
- Liang Chen, MD, PhD
- Tolga Cimen, MD
- Utku Gülan, PhD
- Zihao Zhang, PhD stud.
Funding
- Swiss National Science Foundation (SNF)
- Schwyzer-Winiker Foundation
- Baugarten Foundation
- Swiss Heart Foundation
- USZ Foundation (Wild Grant)
- Swiss Personalized Health Initiative Grant
- ETH – Personalized Health and Related Technologies Grant
- Akdis D, Saguner AM, Shah K, Wei C, Medeiros-Domingo A, von Eckardstein A, Lüscher TF, Brunckhorst C, Chen HSV, Duru F. Sex hormones affect outcome in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy/dysplasia: from a stem cell derived cardiomyocyte-based model to clinical biomarkers of disease outcome. Eur Heart J. 2017 May 14;38(19):1498-1508. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx011. PMID: 28329361.
- Akdis D, Medeiros-Domingo A, Gaertner-Rommel A, Kast JI, Enseleit F, Bode P, Klingel K, Kandolf R, Renois F, Andreoletti L, Akdis CA, Milting H, Lüscher TF, Brunckhorst C, Saguner AM, Duru F. Myocardial expression profiles of candidate molecules in patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy/dysplasia compared to those with dilated cardiomyopathy and healthy controls. Heart Rhythm. 2016;13(3):731-41. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2015.11.010. PMID: 26569459.
- Akdis D, Chen L, Saguner AM, Zhang N, Gawinecka J, Saleh L, von Eckardstein A, Ren J, Matter CM, Hu Z, Chen X, Tanner FC, Manka R, Chen K, Brunckhorst C, Song J, Duru F. Novel plasma biomarkers predicting biventricular involvement in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Am Heart J. 2022 Feb;244:66-76. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj. 2021.10.187. PMID: 34756894.
- Akdis D, Saguner AM, Burri H, Medeiros-Domingo A, Matter CM, Ruschitzka F, Tanner FC, Brunckhorst C, Duru F. Clinical predictors of left ventricular involvement in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Am Heart J. 2020 May;223:34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj. 2020.01.019. PMID: 32146217.
- Akdis D, Saguner AM, Medeiros-Domingo A, Schaller A, Balmer C, Steffel J, Brunckhorst C, Duru F. Multiple clinical profiles of families with the short QT syndrome. Europace. 2018 Jun 1;20(FI1): f113-f121. doi: 10.1093/europace/eux186. PMID: 29016797.
- Akdis D, Chen K, Saguner AM, Stämpfli SF, Chen X, Chen L, Rao M, Haegeli LM, Tanner FC, Brunckhorst C, Song J, Duru F. Clinical Characteristics of Patients with a Right Ventricular Thrombus in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Thromb Haemost. 2019 Aug;119(8):1373-1378. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1688829. PMID: 31183845.
- Gülan U, Saguner AM, Akdis D, Gotschy A, Tanner FC, Kozerke S, Manka R, Brunckhorst C, Holzner M, Duru F. Hemodynamic Changes in the Right Ventricle Induced by Variations of Cardiac Output: A Possible Mechanism for Arrhythmia Occurrence in the Outflow Tract. Sci Rep. 2019 Jan 14;9(1):100. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36614-7. PMID: 30643204.
- Ren J, Chen L, Zhang N, Chen X, Zhao Q, Chen K, Li X, Ruschitzka F, Song J, Duru F.
Plasma testosterone and arrhythmic events in male patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. ESC Heart Fail. 2020 Aug;7(4):1547-1559. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12704. PMID: 32469163. - Costa S, Gasperetti A, Medeiros-Domingo A, Akdis D, Brunckhorst C, Saguner AM, Duru F. Familial Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy: Clinical Determinants of Phenotype Discordance and the Impact of Endurance Sports. J Clin Med. 2020 Nov 23;9(11):3781. doi: 10.3390/jcm9113781. PMID: 33238575.
- Chen S, Chen L, Saguner AM, Chen K, Akdis D, Gasperetti A, Brunckhorst C, Tang H, Guo G, Rao M, Li X, Song J, Hu S, Duru F. Novel Risk Prediction Model to Determine Adverse Heart Failure Outcomes in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022 Jul 5;11(13):e024634. doi: 10.1161/JAHA. 121.024634. PMID: 35766284.
- Costa S, Saguner AM, Gasperetti A, Akdis D, Brunckhorst C, Duru F. The Link Between Sex Hormones and Susceptibility to Cardiac Arrhythmias: From Molecular Basis to Clinical Implications. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Feb 17;8:644279. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.644279. PMID: 33681311.
- Gasperetti A, James CA, Cerrone M, Delmar M, Calkins H, Duru F. Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy and sports activity: from molecular pathways in diseased hearts to new insights into the athletic heart mimicry. Eur Heart J. 2021 Mar 31;42(13):1231-1243. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa821. PMID: 33200174.