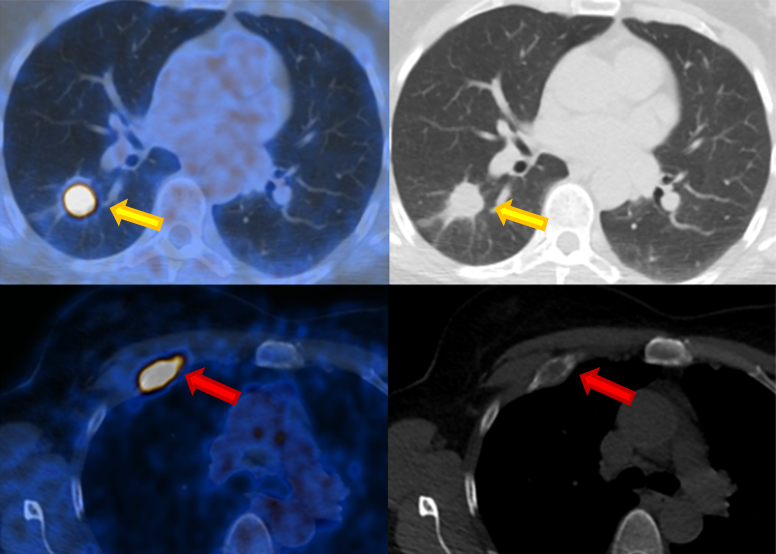
On the axial fused images, focal FDG enhancements can be assigned to the anatomical structures. Thanks to the additional CT scan, the size and local extent of the primary tumor can be determined (yellow arrow). Metastases can also be detected in lymph nodes or other organs, as in this case of a rib metastasis (red arrow).
Preparation and examination
To ensure that the examination is successful, you must not eat anything for at least four hours beforehand and only drink water. Vitamin supplements and “sugarless” chewing gum, sweets or sugar substitutes should also be avoided, as these stimulate the release of insulin, which impairs image quality.
18F-FDGPET for diabetes?
Special precautions are necessary for diabetes. If your blood sugar is difficult to control, please contact us before the examination (Tel.: 044 255 35 55). The blood sugar level must be below 12 mmol/l for an 18F-FDG-PET examination; a value below 7 mmol/l would be ideal.
If you are diabetic, please let us know when planning your PET appointment (Tel.: 044 255 35 55) so that you can be examined in the morning (usually with lower blood sugar levels).
18F-FDGPET in renal insufficiency?
18F-FDGPET can be performed without risks or side effects despite impaired kidney function. However, CT contrast media is not used in the case of renal insufficiency.
18F-FDGPET during pregnancy & breastfeeding?
Due to the increased radiation exposure of the child, an 18F-FDGPET scan is generally not performed during pregnancy. Breastfeeding mothers should not breastfeed their babies for up to six hours after the examination. However, the milk does not have to be discarded, but can be given to the baby via a bottle.
18F-FDGPET risks and side effects?
Only very small amounts of the substance are used in a PET scan, so no interactions with other medications or allergic reactions are to be expected. Due to the short half-life of 18F-FDG, the radiation exposure for the patient is about the same as with a conventional CT scan (approx. 3-10 mSv).
Indications in oncology and infectiology
The following indications for an 18F-FDG PET examinationare established and reimbursed by the health insurance company:
-
- Fever of unknown cause
- Echinococcosis
- Suspicion of large vessel vasculitis
- Suspected infection of vascular grafts
For details see PDF, page 105ff





