How does the surgical robot work?
The Da Vinci robotic system is not an autonomous or pre-programmed robot, but a telemanipulator – a robot-assisted surgical system in which the surgeon uses joysticks to control a camera and up to three 5 to 8 mm diameter working instruments from the console. The camera transmits a three-dimensional image and magnifies the structures in the surgical field up to ten times.
The robot translates the surgeon’s hand movements into instrument movements in the surgical field. The natural trembling of the hand is filtered out in the process and the range of motion of the instruments is clearly superior to that of a human hand. “We perform robot-assisted surgery with more pinpoint accuracy than my hand ever could” says Prof. Daniel Eberli, an experienced Da Vinci surgeon.
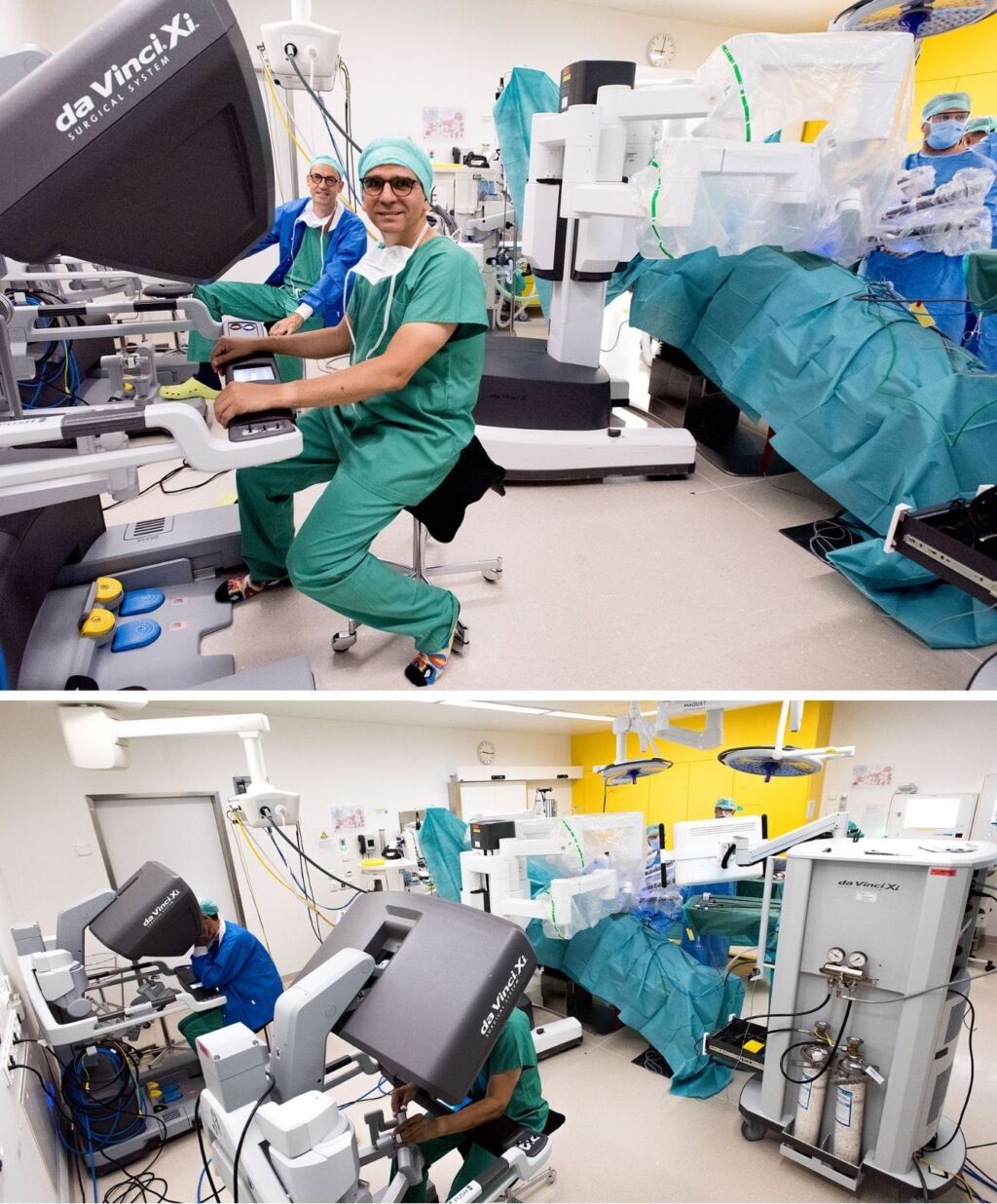
What advantages does the DaVinci Surgical System offer the surgeon?
A surgical robot can be controlled via two consoles. There is a doctor at each console, with only one doctor actively operating while the other monitors. Complex operations lasting hours can thus be performed in a sitting position, which relieves the strain on the surgeon. This also makes it possible to switch between operators without any problems.
The surgeon looks at the organ to be operated on via a high-precision camera that transmits pin-sharp images in 3D optics. As if through a magnifying glass, structures that are otherwise difficult to see, such as nerve tracts, can be identified. In prostatectomy, the removal of the prostate gland, for example, it is much easier to operate in a way that protects the nerves. The likelihood of suffering from erectile dysfunction and incontinence after surgery can be reduced.
The various instruments of the surgical robots are highly precise and delicate. There is an instrument for every purpose – forceps to hold tissue, scissors and scalpels to cut tissue. These can be rotated in all directions with the smallest of movements and thus reach even hard-to-reach regions. Jerky movements are automatically corrected by the robot software, therefore unforeseen injuries are hardly possible.
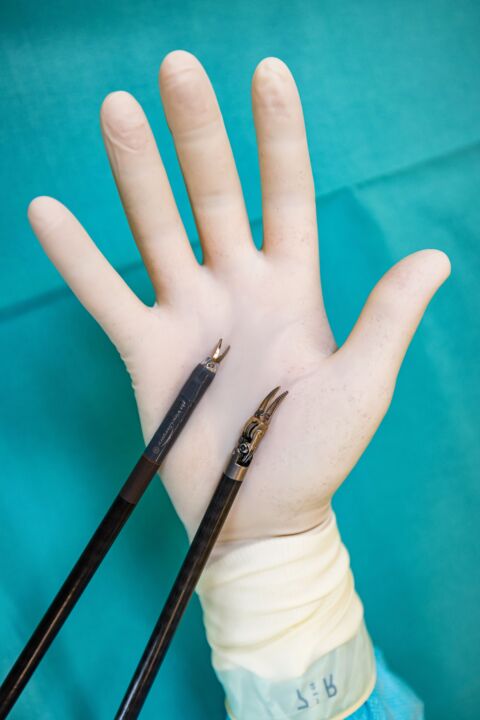
Filigree instruments on the robotic arm enable high-precision surgery
When is DaVinci technology used in urology?
Initially, robotic surgery in urology was used almost exclusively for laparoscopic radical removal of the prostate for prostate cancer. This is still the most common robot-assisted procedure we perform. To date, over 2000 prostatectomies have been performed at the USZ using the DaVinci robot.
However, this modern technology is now being successfully applied in more and more areas.
Surgeries which are nowadays robot-assisted in urology are:
- Radical prostate removal
- Organ-preserving kidney tumor removal
- Kidney removal
- Renal pelvic plastic surgery
- Adrenalectomy
- Radical bladder removal
- Lymph node removal in the pelvis or retroperitoneum
- Ureteral reimplantation
- Complex kidney or ureteral stone removal
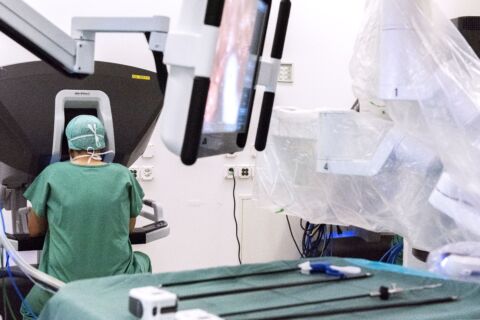
The Da Vinci operator can control the robot from the console with high concentration. Hourly position operations can thus be performed in a sitting position. The image from the robotic camera is greatly magnified and transmitted to the console and several monitors in the operating room.





