Nat commun.
RPA shields inherited DNA lesions for post-mitotic DNA synthesis
Lezaja A, Panagopoulos A, Wen Y, Carvalho E, Imhof R, Altmeyer M. *CCCZ Members in bold
Abstract
The paradigm that checkpoints halt cell cycle progression for genome repair has been challenged by the recent discovery of heritable DNA lesions escaping checkpoint control. How such inherited lesions affect genome function and integrity is not well understood. Here, we identify a new class of heritable DNA lesions, which is marked by replication protein A (RPA), a protein primarily known for shielding single-stranded DNA in S/G2. We demonstrate that post-mitotic RPA foci occur at low frequency during unperturbed cell cycle progression, originate from the previous cell cycle, and are exacerbated upon replication stress. RPA-marked inherited ssDNA lesions are found at telomeres, particularly of ALT-positive cancer cells. We reveal that RPA protects these replication remnants in G1 to allow for post-mitotic DNA synthesis (post-MiDAS). Given that ALT-positive cancer cells exhibit high levels of replication stress and telomere fragility, targeting post-MiDAS might be a new therapeutic opportunity.
Nat Commun. 2021 Jun 22;12(1):3827 doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23806-5
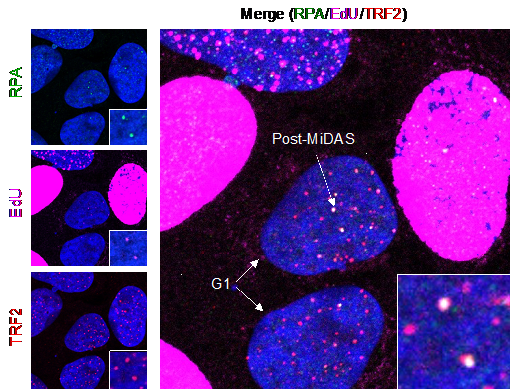
Evidence for single-stranded DNA (marked by the RPA signal in green) and DNA synthesis (EdU signal in magenta) at telomeres (marked by the telomeric protein TRF2 in red) in newly born G1 cells. Such post-mitotic DNA synthesis (post-MiDAS) occurs in response to DNA replication stress, particularly in cancer cells that have activated alternative lengthening of telomeres to achieve replicative immortality.

